A market economy system is a cornerstone of many countries’ economic frameworks. It is characterized by the free exchange of goods and services, largely guided by the principles of supply and demand. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into the intricacies of the market economy system, exploring its defining features, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world examples to provide a holistic understanding of this economic model.
The Fundamentals of a Market Economy System
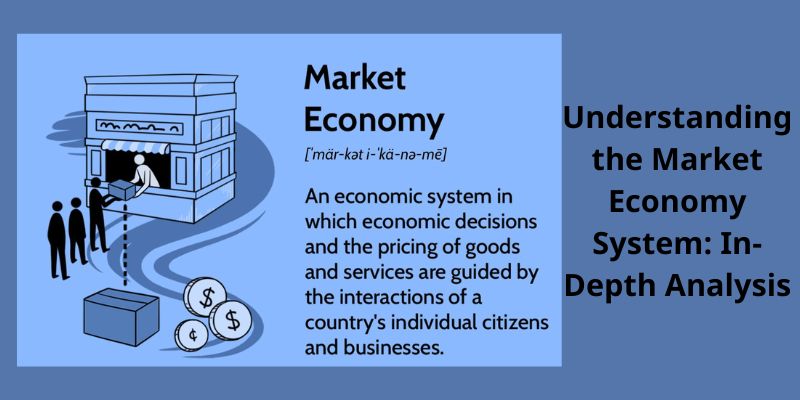
A market economy system, also known as a free-market economy, operates on the principles of voluntary exchange, where decisions regarding investment, production, and distribution are driven by the forces of supply and demand. Unlike command economies, where the government exerts control over economic activities, market economies thrive on minimal government intervention.
Essential Features of a Market Economy System
- Private Property Rights
In a market economy system, individuals and businesses have the right to own and use property as they see fit. This encourages investment and entrepreneurship, as people are motivated to utilize their resources to generate profit.
- Freedom of Choice
Consumers in a market economy system have the freedom to choose what goods and services to purchase. Producers, in turn, have the freedom to decide what products to offer and at what prices. This mutual freedom fosters a competitive environment, driving innovation and efficiency.
- Competition
Competition is a fundamental aspect of a market economy system. Businesses compete to attract consumers by offering better products, lower prices, or superior services. This competition encourages continuous improvement and benefits consumers by providing more options and higher quality products.
- Profit Motive
The profit motive is a key driver in a market economy system. Individuals and businesses seek to maximize their earnings, which incentivizes productivity and economic growth. The pursuit of profit leads to the efficient allocation of resources, as businesses strive to meet consumer demands effectively.
Positive Aspects of a Market Economy System
- Economic Efficiency
A market economy system is inherently efficient because resources are allocated based on supply and demand. Producers are motivated to create goods and services that are in high demand, ensuring that resources are used optimally.
- Positive Change and Strong Technological Development
The competitive nature of a market economy system fosters innovation. Businesses are continuously seeking ways to improve their products and services to gain a competitive edge. This drive for innovation leads to technological advancements and overall economic growth.
- Consumer Sovereignty
In a market economy system, consumers have significant influence over what is produced. Their preferences and purchasing choices direct the activities of producers. This consumer sovereignty ensures that goods and services are tailored to meet the needs and desires of the population.
- Flexibility and Adaptability
A market economy system is highly adaptable to changing circumstances. Producers can quickly respond to shifts in consumer preferences, technological advancements, and market conditions. This flexibility allows the economy to adjust smoothly to external shocks and changes.
Drawbacks of a Market Economy System
- Income Inequality
One of the primary criticisms of a market economy system is the potential for income inequality. Because rewards are based on productivity and success, there can be significant disparities in income and wealth distribution. This inequality can lead to social tensions and economic instability.
- Market Failures
Despite its efficiency, a market economy system is not immune to market failures. These occur when the free market fails to allocate resources efficiently, leading to negative outcomes such as pollution, public goods underproduction, and monopolies. In these instances, it may be essential for the government to step in and rectify these failures.
- Consumer Exploitation
In the absence of regulation, businesses in a market economy system may engage in practices that exploit consumers. For example, false advertising, price gouging, and the sale of unsafe products can occur if there are no safeguards in place to protect consumers.
- Boom and Bust Cycles
Market economy systems are prone to economic cycles of boom and bust. Periods of rapid economic growth can be followed by sharp contractions and recessions. These cycles can lead to economic instability and uncertainty for businesses and consumers.
Real-World Examples of Market Economy Systems
The United States
The United States is often cited as a prime example of a market economy system. With a strong emphasis on private property rights, competition, and minimal government intervention, the U.S economic success is fueled by innovation and entrepreneurship.. The country’s dynamic economic landscape has led to significant technological advancements and economic growth. However, it also faces challenges such as income inequality and periodic economic downturns.
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is another example of a market economy system. Known for its free-market policies, Hong Kong has one of the most open economies in the world. The absence of tariffs and minimal regulation has attracted businesses and investors, making it a global financial hub. Despite its economic success, Hong Kong grapples with issues such as housing affordability and income disparity.
Conclusion
The market economy system is a powerful and dynamic economic model that has driven growth and innovation in many countries. Its core principles of private property rights, competition, and the profit motive create an environment that encourages efficiency and adaptability. However, it is not without its drawbacks, including income inequality, market failures, and economic cycles.
By understanding the advantages and the remaining limitations of the market economy system, we can better appreciate its impact on our lives and the global economy. As we move forward, it is crucial to address the challenges associated with this economic model to ensure a more equitable and sustainable future.

Để lại một bình luận